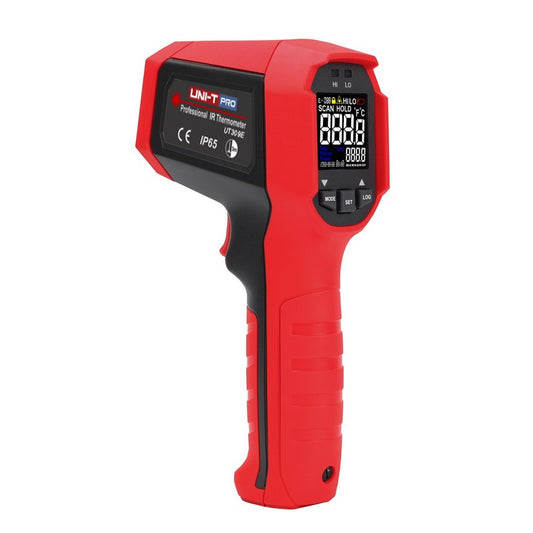
Infrared Thermometers
Sort by
Comprehensive Buyer's Guide to Infrared Thermometers
Introduction
Infrared thermometers have revolutionized temperature measurement across numerous industries by enabling quick, accurate, non-contact readings. Unlike traditional contact thermometers that require physical touch with the surface being measured, infrared thermometers detect the thermal radiation (infrared energy) emitted by objects and convert it into temperature readings.
How Infrared Thermometers Work
Infrared thermometers operate based on the principle that all objects emit infrared radiation proportional to their temperature. The thermometer's sensor detects this radiation, allowing for temperature measurement without physical contact. This makes them invaluable for measuring:
- Hot or dangerous surfaces where contact would be unsafe
- Moving objects that can't be touched during operation
- Targets that might be contaminated or damaged by contact
- Multiple points quickly for efficiency in inspections
- Hard-to-reach surfaces that are inaccessible for contact measurement
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their advantages, it's important to understand what infrared thermometers cannot measure accurately:
- Air or gas temperatures: Infrared thermometers measure surface temperatures, not ambient air temperature.
- Through glass or transparent surfaces: They measure the surface temperature of the glass itself, not what's behind it.
- Highly reflective or shiny surfaces: These can reflect infrared radiation from other sources, causing inaccurate readings without proper emissivity adjustment.
- Very small objects: The measurement spot size must be completely filled by the target for accurate readings.
- Objects behind steam, dust, or smoke: These can interfere with the infrared signal.
Understanding these limitations is crucial for selecting the right tool for your specific application needs.
Understanding the Distance-to-Spot Ratio
The Distance-to-Spot ratio (written as D/S) is perhaps the most critical specification to consider when selecting an infrared thermometer. This ratio determines how well the device can measure temperature from a distance.
- Basic (10/1 - 12/1 ratio): Suitable for general applications where measurements are taken from relatively close distances. A 10/1 ratio means at 10 inches away, the device measures a 1-inch diameter spot.
- Intermediate (20/1 ratio): Ideal for moderate distance readings, offering a good balance between range and precision.
- Professional (50/1 ratio): Enables accurate temperature measurements from significant distances, perfect for hard-to-reach or hazardous areas.
- High-Precision (55/1 ratio and above): Provides exceptional accuracy from substantial distances, essential for specialized industrial applications.
For the most demanding professional applications, look for thermometers with distance-to-spot ratios of 50/1 or higher, which allow for precise measurements even at considerable distances.
Temperature Range and Accuracy
When evaluating infrared thermometers, consider both the temperature range and the device's accuracy:
- Temperature Range: Professional-grade infrared thermometers typically offer ranges from -50°C to 850°C, with high-end models extending up to 2200°C. Consider your specific application requirements when choosing an appropriate range.
- Accuracy: Look for thermometers with accuracy ratings of ±1.0°C/±1.0% or better. Top-tier models may offer enhanced accuracy of ±0.5°C or even greater precision for critical measurements.
- Repeatability: This indicates how consistent the measurements are when taken repeatedly under the same conditions. Professional models typically offer repeatability of ±0.5% or better.
Adjustable Emissivity
Emissivity refers to a material's ability to emit infrared energy. Different surfaces have different emissivity values, affecting measurement accuracy:
- Fixed Emissivity (typically 0.95): Suitable for basic applications and common surfaces.
- Adjustable Emissivity (0.1-1.0): Essential for professional use across various materials and surfaces. This feature allows calibration for different surface types, from highly reflective metals to matte finishes, ensuring accurate readings regardless of the target material.
Without proper emissivity adjustment, measurements on shiny or reflective surfaces can be significantly inaccurate, often reading lower than the actual temperature.
Essential Features for Professional Applications
Display Technology
- LCD Displays: Standard on most models, providing clear, easy-to-read measurements.
- Color EBTN Displays: Offer enhanced visibility in various lighting conditions and can display additional information simultaneously.
- LED Indicators: Visual high/low temperature alerts that provide immediate feedback without having to read the display.
Measurement Modes
- MAX/MIN/AVG/DIFF: Records maximum, minimum, and average readings, as well as differential between measurements.
- Data Hold: Freezes the current reading on display for recording purposes.
- Continuous Scanning: Allows for monitoring temperature changes over time.
- Surface Dew Point Detection: Critical for HVAC and building envelope analysis.
- Surface Heat Conduction Detection: Important for identifying thermal bridges and insulation issues.
Data Management
- Data Storage: Look for models that can store multiple readings (99+ data points) for later analysis.
- Date and Time Stamping: Helps with documentation and tracking measurements over time.
- USB Connectivity: Allows for data transfer to computers for further analysis and reporting.
- Export Capabilities: Advanced models support data export in PDF and CSV formats for professional documentation.
Additional Measurement Options
- Type K Thermocouple Support: Provides an additional contact temperature measurement method for verification and specific applications.
- Ambient Condition Monitoring: Measures relative humidity, wet bulb temperature, and ambient temperature for comprehensive environmental assessment.
Durability and Design Considerations
Professional environments demand robust equipment:
- IP Ratings: Look for IP65 or higher for protection against dust and water ingress.
- Drop Protection: Models with 1-3 meter drop resistance ensure durability in demanding work environments.
- Ergonomics: Comfortable grip design for extended use.
- Battery Life: Consider operational time and battery type for field applications.
- Mounting Options: Tripod mounting capabilities for hands-free operation and consistent measurement points.
- Response Time: Fast response times (250ms or less) are crucial for dynamic environments and efficient workflows.
Specialized Applications
Different industries have specific requirements:
HVAC/R
- Wide temperature range (-50°C to 650°C)
- Dew point detection
- K-type thermocouple for vent temperature verification
Electrical Inspection
- High temperature capability (up to 850°C or higher)
- Small spot size for detailed component analysis
- High/low temperature alarms for quick identification of potential issues
Building Inspection and Energy Efficiency
- Thermal bridge detection
- Surface heat conduction analysis
- Data storage and reporting features
Industrial Manufacturing
- Extended high-temperature range (up to 2200°C)
- High distance-to-spot ratio (50/1 or greater)
- Scheduled and monitoring measurement capabilities
Food Service and Processing
- Moderate temperature range (-30°C to 250°C)
- Fast response time
- Waterproof construction for cleaning environments
Best Practices for Accurate Measurements
To get the most from your infrared thermometer:
- Match the tool to the distance: Ensure you're using a thermometer with an appropriate distance-to-spot ratio for your measurement distance.
- Adjust emissivity: Set the correct emissivity value for the material being measured.
- Measure perpendicular: For best accuracy, aim the thermometer as close to perpendicular to the surface as possible.
- Fill the measurement spot: Ensure the target completely fills the measurement spot for accurate readings.
- Avoid interference: Beware of steam, dust, or strong electromagnetic fields that can affect readings.
- Use comparative measurements: When absolute accuracy is critical, take comparative readings or verify with a contact thermometer.
Warranty and Support Considerations
Professional tools are investments that should be protected:
- Warranty Period: Look for manufacturers offering comprehensive warranties.
- Calibration Services: Consider availability of professional calibration to maintain accuracy.
- Accessories: Evaluate included and optional accessories such as carrying cases, K-type probes, and tripod mounts.
Conclusion
When selecting an infrared thermometer, focus on matching the specifications to your specific applications. For professionals requiring versatility, accuracy, and reliability, look for models with high distance-to-spot ratios (50/1 or greater), wide temperature ranges, adjustable emissivity, and comprehensive data management features. These capabilities ensure accurate measurements across various materials and environments, making your infrared thermometer a valuable addition to your professional toolkit.
By understanding both the capabilities and limitations of infrared thermometry technology, you'll be equipped to select an infrared thermometer that delivers precise, reliable performance for your specific application needs.